Today’s lesson goal: Understand the concept, purpose, and functionality of Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) in network design and management.
Introduction to VLANs
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a network concept that allows multiple logical networks to coexist on a single physical network infrastructure. It’s used in various network environments to improve scalability, security, and network management.
How VLANs Work
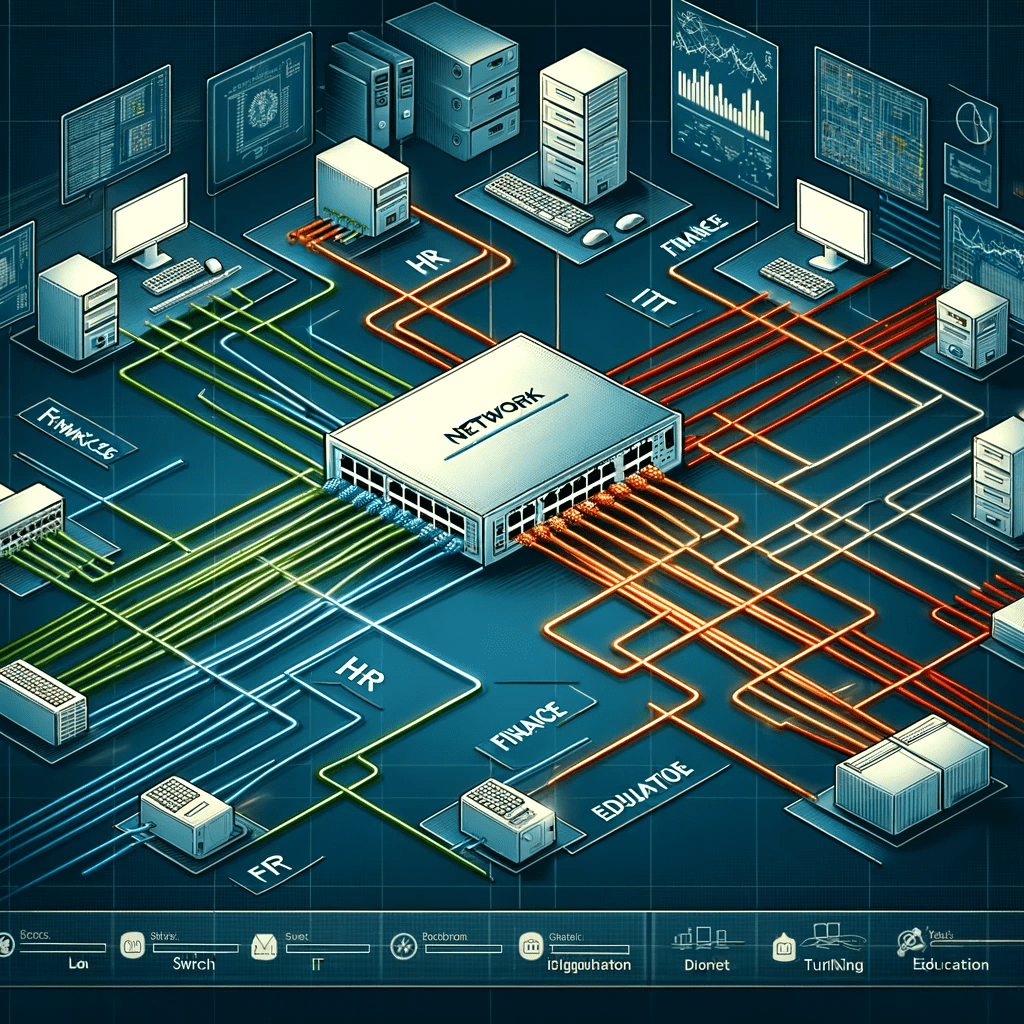
- Segmentation: VLANs divide a physical network into multiple, isolated logical networks. Each VLAN is treated as a separate entity, allowing for increased security and efficient traffic management.
- Tagging: Network devices, like switches, use VLAN tags (specifically, IEEE 802.1Q standard) to distinguish between different VLANs’ traffic. When a data packet moves through a VLAN-aware switch, the switch adds a VLAN tag to the packet, indicating its VLAN membership.
- Inter-VLAN Routing: Communication between VLANs is not inherently possible as they are isolated. Inter-VLAN routing, typically performed by Layer 3 switches or routers, is necessary for data exchange between different VLANs.
- Trunking: Trunk ports on network switches are configured to carry traffic for multiple VLANs. Trunking protocols, like 802.1Q, encapsulate VLAN traffic, allowing it to traverse a shared network backbone.
Benefits of VLANs
- Security: By segmenting networks into VLANs, sensitive data and resources can be isolated, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Performance: VLANs can reduce network congestion by separating broadcast domains, leading to improved network performance.
- Flexibility: VLANs offer the flexibility to group users based on logical functions rather than physical location, making network management easier.
- Cost-Efficiency: VLANs enable the efficient use of network resources, reducing the need for additional physical hardware.
Real-World Applications
- Corporate Networks: In a business setting, VLANs can separate departments (like HR, Finance, and IT) to enhance security and manageability.
- Educational Institutions: VLANs can be used to separate administrative, faculty, and student networks.
- Data Centers: VLANs provide isolation between different clients or services within a shared data center environment.
Supplementary Resource
For a more visual and interactive understanding, watch this YouTube video: VLANs Explained.
(c) 2014 Knowledge-Brothers.com – V00.01